Matsuri has origins in Shintoism. It was meant to celebrate kami, or Shinto “gods”/deities. Further, matsuri was meant to celebrate a local shrine’s kami, or a seasonal or historical event. While most Japanese individuals do not regard themselves as being religious today, many of the practices of Shintoism have become ingrained in Japanese culture; this is why matsuri is still celebrated today.
One prominent matsuri in Japan is natsu-matsuri, which are the festivals that occur in the summer season (July and August). This is the matsuri celebrated by GVJCI every June.
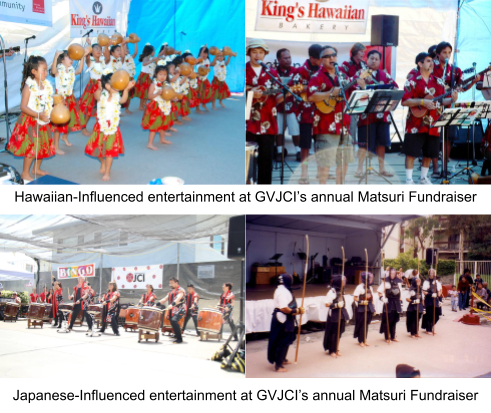
Despite the fact that matsuri differ based on when and where they occur in Japan, many characteristics remain consistent. Matsuri usually features mikoshi, or palanquins that are small portable shrines; the local shrine’s kami is said to be carried around the town in mikoshi during the festival. Another feature of matsuri is dashi and yatai, or decorated festival floats. These floats are meant to resemble mountains, which in its Shinto origin were believed to be where kami reside. While mikoshi carry the kami honored at the local shrine, dashi and yatai are built more generally for all the kami that live in the mountains. Dashi and yatai usually also feature a Taiko, or drum, stand. Other common characteristics of matsuri include hanabi, or fireworks, games and activities, and food.





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
